JShell default package:
Now we will discuss the package related concept, by default how many packages are available in jshell.
Let's see a few examples:
EX.1:-
jshell> Math.sqrt(4)
$4 ==> 2.0
| created scratch variable $4 : double
EX.2:-
jshell> Math.max(10,20)
$5 ==> 20
| created scratch variable $5 : int
EX.3:-
jshell> Math.random()
$6 ==> 0.6956946870985563
| created scratch variable $6 : double
- Here you can see we didn't include any package in the jshell still Math class is working because of the java.lang package which is by default available to jshell.
Let's check the whether this code will work in jshell or not?
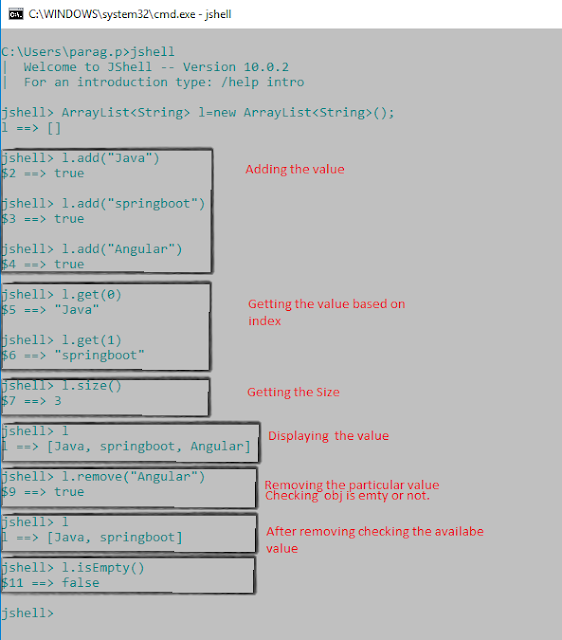
jshell> ArrayList<String> l=new ArrayList<String>();
l ==> []
As ArrayList, is available in java.util package. So how it is working even we are not importing java.util package in jshell.
By seeing the output it is clear that java.util package is also available to jshell, that's why it has created the empty ArrayList obj.
We can do multiple operations on ArrayList obj like add, remove, getting the size of obj.
Refer the below operation:
There is one question that :
Q1. How many packages are imported by default to jshell?
So, this is all about packages.
Jshell Compiler
Internally jshell having Java compiler which is responsible to check syntax. If any violation in syntax then we will get Compile time error which is exactly the same as normal compile time errors.
Below is the example of compile-time error:
EX.2
In this case, jshell compiler will give the compile-time error because we have typed (Sytsem) instead of System and it is not recognized by jshell compiler hence it throws compile time error.
Let's Watch the difference between jshell compiler and java normal compiler:-
In our program, if there is any chance of getting checked exceptions compulsory we required to handle either by try-catch or by throws keyword. Otherwise, we will get a Compile time error.
But in the case of Jshell, jshell itself will take care of these and we are not required to use try-catch or throws. Thanks to Jshell.
import Java.io.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter("abc.txt");
pw.println("Hello");
}
}
When we run this java program using normal java compiler, then we will get the compile-time error.
but if run the same program in jshell we will not get the compile-time error.
below is the code for jshell
jshell> PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter("abc.txt");pw.println("Hello");pw.flush();
pw ==> Java.io.PrintWriter@e25b2fe
Conclusions:
- From the jshell we can execute any expression, any Java statement.
- Most of the packages are not required to import to the Jshell because by default already available to the jshell.
- Internally jshell use Java compiler to check syntaxes
- If we are not handling any checked exceptions we won’t get any compile time errors, because jshell will takes care.